Bimatoprost is an ophthalmic solution used to lower intraocular pressure in individuals dealing with open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension and cosmetically to treat hypotrichosis. This article covers the indications and mechanism of action of adverse effects.
Reduction of Intraocular pressure (IOP)
Bimatoprost is an anti-glaucoma formulation that belongs to a group of medications known as prostamides. The eye drops are used to reduce high pressure in the eye. The ophthalmic solution may be used on its own or with other medications called beta blockers, which also reduce pressure. Your eye contains a clear liquid that feeds inside of the eye. Fluid is constantly being drained of the eye, and new fluid is being made to replace this. If the fluid can’t drain out quickly enough, pressure inside the eye builds up. It treats high pressure in the eye (ocular hypertension), which helps with glaucoma. High pressure happens when excessive fluids build up inside your eye. Bimatoprost ophthalmic solution helps to drain the fluid.
Mechanism of action
Prostaglandin analog, including Bimatoprost, increases the amount of drained liquid. This reduces the pressure inside of the eye. If the high pressure is not reduced, it could lead to glaucoma and eventually damage your sight. It is shown that lowering IOP in patients with ocular hypertension and glaucoma may cause a significant reduction in the risk of ocular disease progression.
Lowering IOP lowers the risk of visual field loss in patients with ocular hypertension and glaucoma. Bimatoprost is a potent and highly efficacious monotherapy that allows many patients to achieve low target pressures. Moreover, several clinical trials have shown that Bimatoprost, when used as a single agent, lowers IOP more effectively than the combination medicine. Bimatoprost is a prostamide that reduces IOP by increasing presumed trabecular meshwork and uveoscleral outflow.
Enhancement of eyelash growth
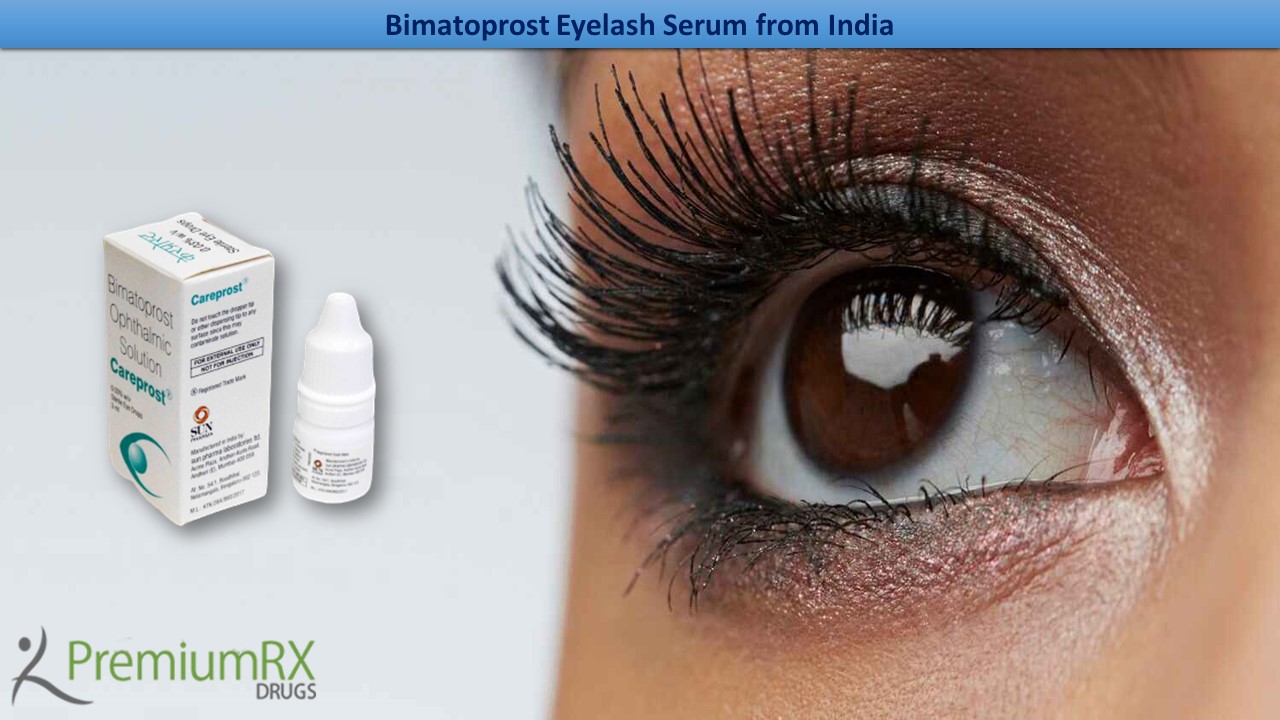
Hypotrichosis is defined as less than a normal amount of hair and eyelashes; hypotrichosis is the term for an inadequate number of lashes. Eyelashes provide a protective barrier for the eyes, wind, sun rays, perspiration, and foreign bodies. They act like the whiskers on a cat or a mouse. They are quite sensitive to touch and signal a warning sign when an object is near the eye, which in turn causes the eye to close reflexively. Along with the protective purpose of eyelashes, longer and fuller eyelashes are cosmetic attractions. The absence of well-framed lashes removes one of the salient features of a normal facial appearance. A set of fuller eyelashes is also considered a sign of feminity and beauty in most cultures.
Eyelashes hypotrichosis is a condition caused by an inadequate number of eyelashes. Hypertrichosis of eyelashes, characterized by excessive lash growth, is a particular phenomenon associated with ophthalmic prostaglandin. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) USA approved Bimatoprost 0.03% solution for increasing eyelash length, thickness, and darkness in patients with hypotrichosis of eyelashes.
Bimatoprost increases eyelash length, thickness, and darkness in patients with hypotrichosis of the eyelashes. This article will discuss the effects of Bimatoprost on eyelashes, which has been more extensively studied in hypertrichosis of eyelashes.
The mechanism of action
The mechanism by which bimatoprost 0.03% ophthalmic solution affects eyelash growth is not completely understood. Bimatoprost causes a significantly greater proportion of anagen follicles and a decrease in telogen (resting phase) and late catagen follicles (Transitional phase of the hair growth cycle between anagen and telogen), suggesting that careprost bimatoprost eyelash growth solution extends the duration of the growth phase. Bimatoprost can potentially influence the growth cycle of eyelashes by stimulating follicles to enter the growth phase earlier and remain there longer. Eyelash hair follicles are known to be proportionally higher during the resting phase, which supports the effectiveness of bimatoprost solution for hypotrichosis of the eyelashes.
Conclusion
Bimatoprost is a member of a new class of drugs that reduces IOP. It is a mild stimulant of aqueous humor flow, both day and night. It is believed that enhancement of uveoscleral outflow, the primary mechanism of action of Bimatoprost, is partly responsible for the ocular hypotensive effect of the product. When it comes to eyelash growth, Careprost bimatoprost most likely stimulates the telogen phase (resting follicles) to the anagen phase (growing follicles). It also extends the growth phase of eyelashes, which leads to an increase in lash length. The ophthalmic solution is generally safe and well-tolerated when applied on the base of the eyelashes at the lid margin with minimum side effects.
Marie
Latest posts by Marie (see all)
- Revize Micro Gel 0.025% | Uses, Price, Side effects - April 9, 2025
- What is Evalon Cream: How to Apply, Benefit, who Can Use - April 4, 2025
- Understanding Avanair 200 mg: A Comprehensive Guide - April 4, 2025